My target price for GETY is ~$4.00 / share over a ~12/14 month hold period, generating a ~30%+ IRR at 3:1 risk/reward, assuming the merger with Shutterstock receives regulatory approval.

The recently announced merger between Getty Images and Shutterstock is an interesting case study into two companies grappling with massive technological disruption.
At first glance, this transaction is an attempt to merge two failing entities in a desperate bid to keep them afloat. With AI-generated images becoming widespread so quickly, it seems like we’re witnessing a scenario reminiscent of the downfall of Record Stores or Blockbuster.
Upon further investigation, the merger creates value through freeing up Getty’s balance sheet to invest in and embrace generative AI, while maintaining premium, rights-managed images catered to a specific client base. The merged entity has the ability to swiftly de-lever and deploy capital to further innovate in the space.

Future Share Price Analysis
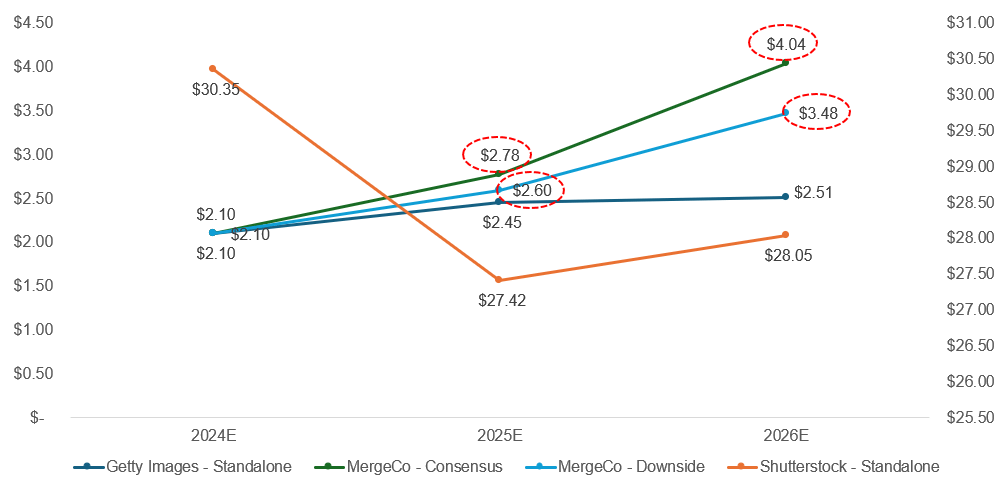
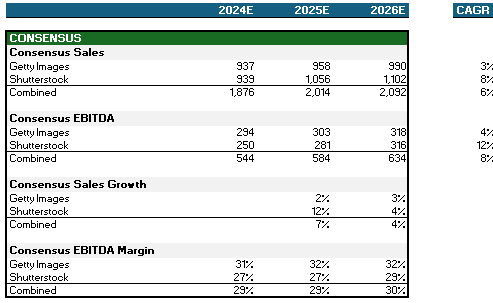
Comparing standalone Getty at it’s current EV/EBITDA multiple of ~7.7x with a pro-forma MergeCo multiple at ~6.0x, there is still significant upside in the stock over the next 12-18 months
Value Creation & IRR Analysis
Over a ~14 month hold period, assuming Consensus levels and ~2/3 of SG&A synergies achieved, you can generate a 36% IRR at an eroded multiple of ~6.0x (assuming a weighted average of SSTK and GETY). Even with dis-synergies of ~$10mm your IRR generated is 17%.
There exists significant upside to the extent the combined company maintains a valuation multiple at the same level as GETY on a standalone basis.
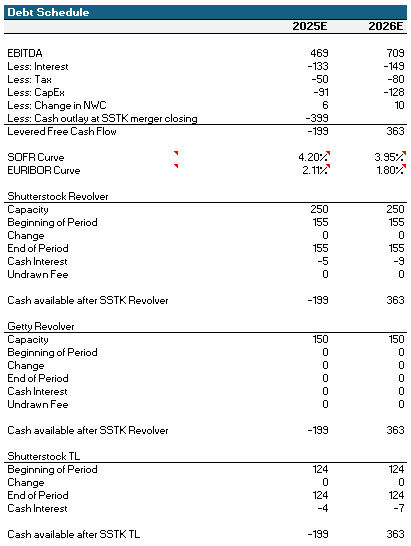
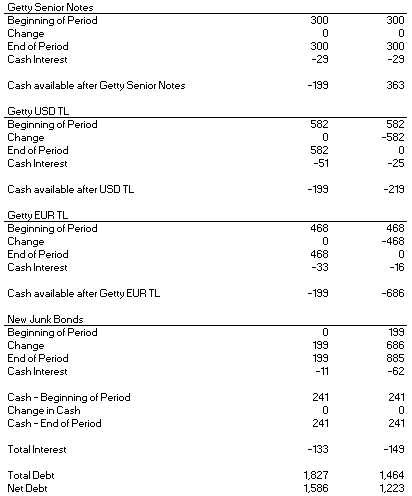
GETY has ~$1bn of debt in USD and EUR Term Loans maturing in 2026. Even with a slug of junk bond debt taken out to i) finance the deal and ii) pay the loans back at maturity, the company is still able to de-lever to sub-2.0x in 2026E.
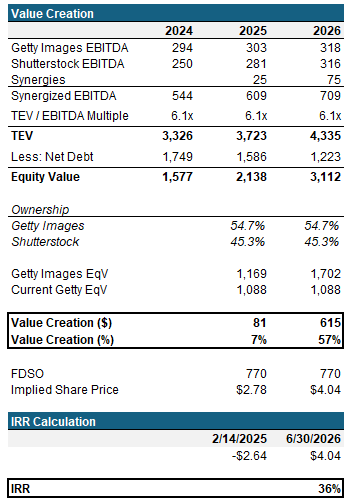
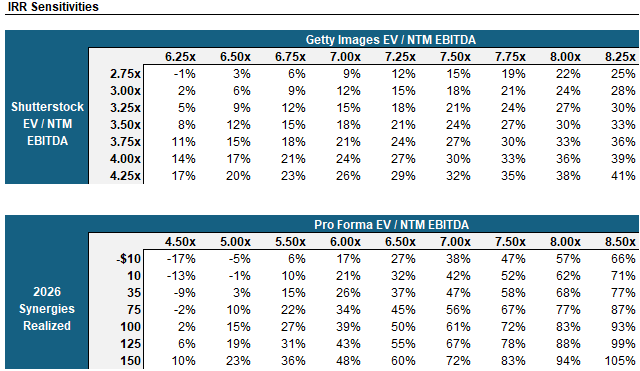
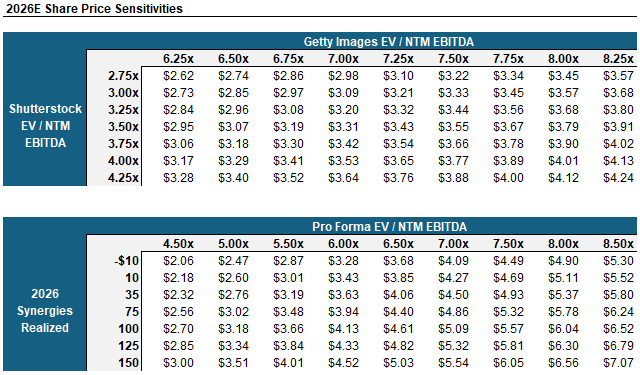
Getty expects cost synergies of $75-$100mm within the first year
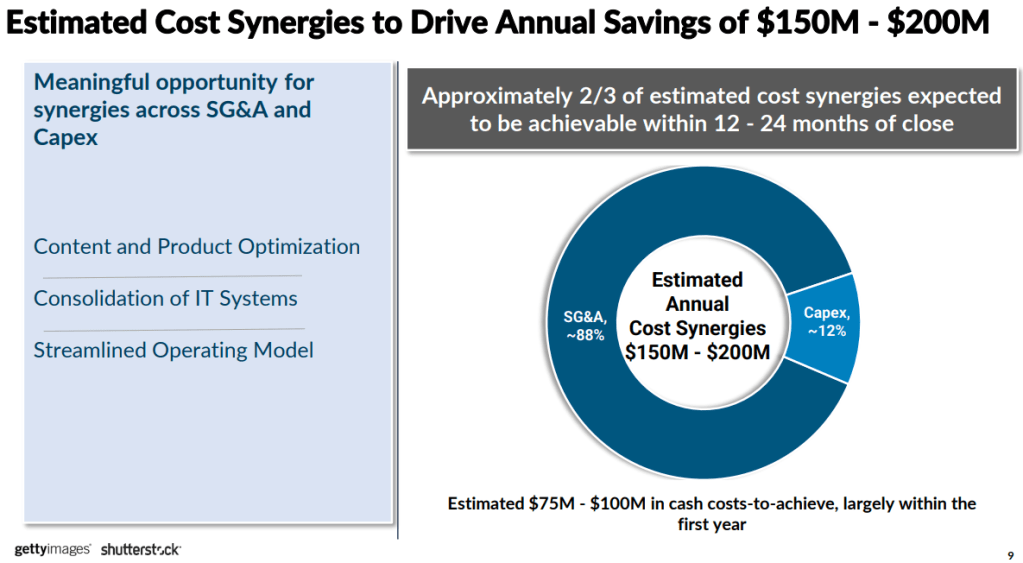
GETY’s EV/ NTM EBITDA low since 2022 is in the ~7.3x range, while SSTK has traded at ~3.7x at their 3-year low.
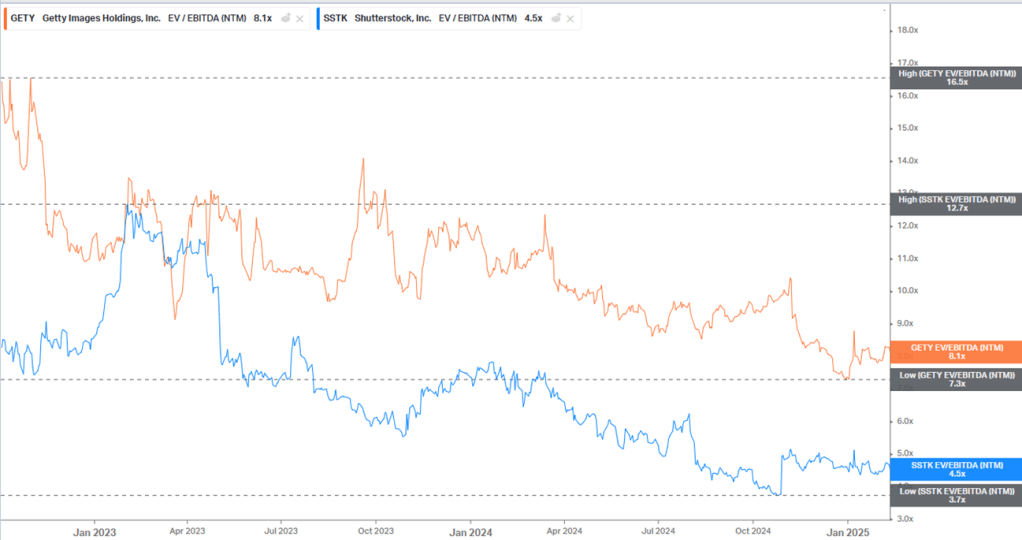
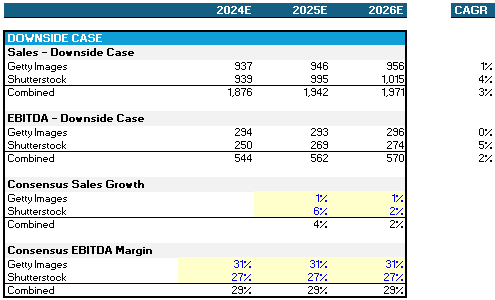
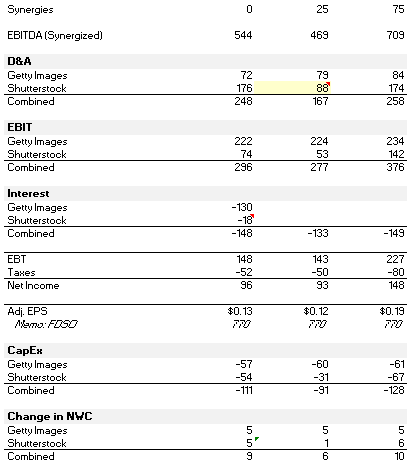
2026E Adj. EPS Accretion of ~37% based on Consensus figures and $75mm synergy achievement. Additional debt paydown assumptions below and in the attached model. Assuming the downside case of flat standalone margins and topline growth at 50% of Consensus, Adj. EPS and neutral.
AI and Photo Copyrighting: A Threat to Shutterstock and Getty Images
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized numerous industries, from healthcare to entertainment, and the realm of visual media is no exception. Stock photography giants like Shutterstock and Getty Images, which have long dominated the market for licensed images, are now facing unprecedented challenges due to the rise of AI-generated imagery and evolving copyright concerns. These developments threaten the traditional business models of stock photography platforms, raising questions about their long-term viability in an increasingly AI-driven world.
The Rise of AI-Generated Imagery
AI technologies, such as DALL-E, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion, have made it possible to generate high-quality, photorealistic images from simple text prompts. These tools have democratized content creation, allowing individuals and businesses to produce custom visuals without the need for professional photographers or expensive licensing fees. For Shutterstock and Getty Images, which rely on a vast library of human-created photographs and a subscription-based revenue model, this represents a significant disruption.
Unlike traditional stock photography, AI-generated images can be created on demand, tailored to specific needs, and produced at a fraction of the cost. This eliminates the need for users to browse through thousands of pre-existing images or pay for licenses that may not perfectly align with their vision. As AI tools become more sophisticated and accessible, they are increasingly viewed as a viable alternative to stock photography platforms, potentially reducing the demand for Shutterstock and Getty Images’ services.
Copyright Challenges
The intersection of AI and copyright law further complicates the situation for stock photography companies. Traditional copyright protections are designed to safeguard the work of human creators, but AI-generated images blur these lines. In many jurisdictions, the legal status of AI-created content remains unclear. For instance, can an AI-generated image be copyrighted? If so, who owns the rights—the developer of the AI, the user who provided the prompt, or no one at all?
This ambiguity poses a dual threat to Shutterstock and Getty Images. On one hand, it undermines their ability to compete with AI-generated content, which may not be subject to the same licensing restrictions as human-created photographs. On the other hand, it raises concerns about the potential misuse of their own libraries. AI models are often trained on vast datasets of images scraped from the internet, including those from stock photography platforms. If these models generate images that resemble copyrighted works from Shutterstock or Getty Images, it could lead to legal disputes over ownership and compensation.
In response, both companies have taken steps to address these challenges. Shutterstock, for example, has partnered with OpenAI to integrate AI-generated content into its platform, allowing it to offer both human-created and AI-generated images. Getty Images, meanwhile, has pursued legal action against Stability AI, the developer of Stable Diffusion, alleging that its AI was trained on millions of Getty’s copyrighted images without permission. These actions highlight the tension between embracing AI as a tool and protecting their core business interests.
Economic Implications for Stock Photography
The economic implications of AI and copyright issues are profound for Shutterstock and Getty Images. Stock photography has historically been a lucrative industry, with companies charging premium prices for high-quality, professionally curated images. However, the proliferation of free or low-cost AI tools threatens to erode this pricing power. Small businesses, content creators, and even large corporations may opt for AI-generated images over licensed stock photos, reducing the revenue streams that these companies rely on.
Furthermore, the rise of AI could devalue the work of professional photographers who contribute to stock photography libraries. As AI-generated images flood the market, photographers may see reduced demand for their services, leading to fewer submissions to platforms like Shutterstock and Getty Images. This could create a vicious cycle, diminishing the size and quality of their image libraries and further weakening their competitive position.
Adapting to the AI Revolution
To survive in this rapidly evolving landscape, Shutterstock and Getty Images must adapt their business models to incorporate AI while addressing copyright concerns. One potential strategy is to position themselves as leaders in ethical AI-generated content. By developing or partnering with AI tools that are trained on legally sourced datasets, they can offer a hybrid model that combines the best of human creativity and machine efficiency. This approach would allow them to maintain relevance in the market while upholding their commitment to protecting intellectual property.
Another avenue for adaptation is to focus on niche markets that AI cannot easily replicate. For example, highly specialized or culturally significant imagery, such as historical archives or editorial photography, may remain in demand even as AI-generated content grows. By emphasizing their expertise in these areas, Shutterstock and Getty Images can differentiate themselves from AI competitors and retain a loyal customer base.
Both companies have started to advocate for clearer copyright regulations in the AI era. By working with policymakers and industry stakeholders, they can help shape laws that protect human creators while allowing for innovation in AI-generated content. This proactive approach could mitigate some of the legal uncertainties they currently face and provide a more stable foundation for their businesses.
The rise of AI and the associated copyright challenges represent a threat to Shutterstock and Getty Images, two titans of the stock photography industry. As AI-generated imagery becomes more prevalent and affordable, these companies risk losing market share and relevance unless they adapt to the changing landscape. By embracing AI as a tool, focusing on niche markets, and advocating for clearer copyright protections, they can navigate this disruption and continue to thrive.
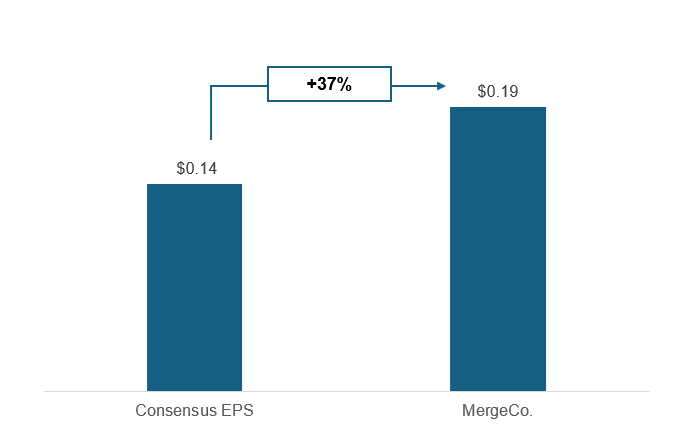
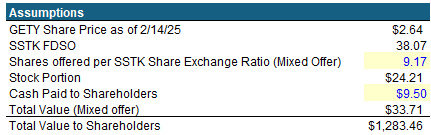
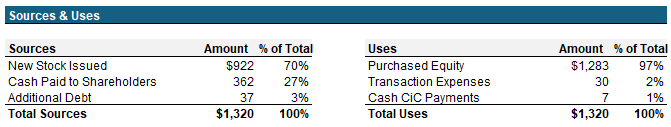
Pro Forma Capitalization and Sources & Uses
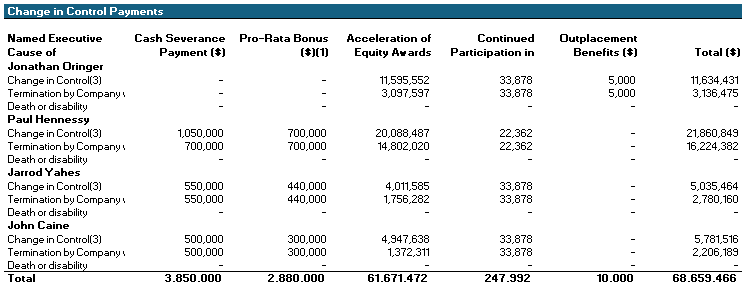
DEF 14A – Shutterstock Inc. – BamSEC



Leave a comment